AIUC-1 operationalizes Cisco’s AI Security Framework

We are excited to announce Cisco as a technical contributor to AIUC-1. The standard will operationalize Cisco's Integrated AI Security and Safety Framework (AI Security Framework), enabling more secure AI adoption.
AI risks are no longer theoretical. We have seen incidents ranging from swearing chatbots to agents deleting codebases. The financial impact is significant: EY's recent survey found 64 percent of companies with over US$1 billion in revenue have lost more than US$1 million to AI failures.
Enterprises are looking for answers on how to navigate AI risks.
Organizations also don't feel ready to tackle these challenges, with Cisco’s 2025 AI Readiness Index revealing only 29 percent of companies believe they are adequately equipped to defend against AI threats.
Yet current frameworks address only narrow slices of the risk landscape, forcing organizations to piece together guidance from multiple sources. This makes it difficult to build a complete understanding of end-to-end AI risk.
Cisco's AI Security Framework addresses this gap directly, providing a more holistic understanding of AI security and safety risks across the AI lifecycle.
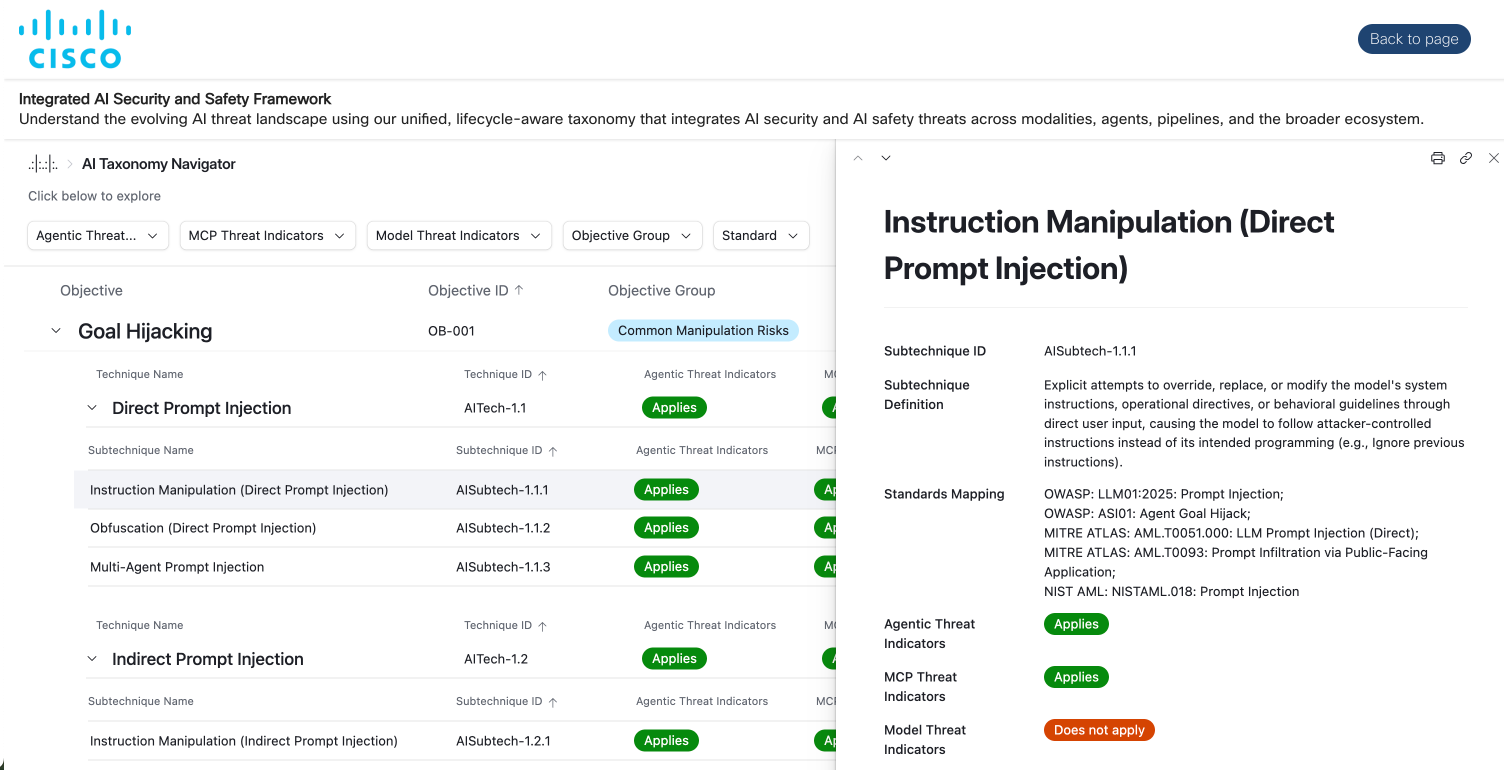
The framework breaks down the complex landscape of AI security into one that works for multiple audiences. For example, executives can operate at the level of attacker objectives, whereas security leads can focus on specific attack techniques.
Read more about Cisco’s AI Security Framework here and navigate the taxonomy here.
AIUC-1 operationalizes the framework enabling secure AI adoption
When evaluating AI agents, AIUC-1 will incorporate the security and safety risks from Cisco's Framework. This integration will be direct: risks highlighted in Cisco's Framework map to specific AIUC-1 requirements and controls.
For example, technique AITech-1.1 (direct prompt injection) is actively mitigated by integrating AIUC-1 requirements B001 (third-party testing of adversarial robustness), B002 (detect adversarial input), and B005 (implement real-time input filtering). A detailed crosswalk document mapping the framework to AIUC-1 will be released, once ready, to help organizations understand how to operationally secure themselves.
This partnership positions Cisco alongside organizations including MITRE, the Cloud Security Alliance, and Stanford's Trustworthy AI Research Lab as technical contributors to AIUC-1, collectively building a stronger and more holistic understanding of AI risk.
Read more about how AIUC-1 operationalizes emerging AI frameworks here.
Latest articles



